 ATTENTION: Want to Learn Affiliate Marketing from Successful Affiliates?
Join this FREE community where successful marketers share their secrets!
Learn directly from highly successful affiliate marketers
Access free, actionable training content regularly
Connect with an active community of over 5,000 members
Network with multiple six-figure earning affiliates
Get your questions answered by real experts
JOIN FREE NOW!
ATTENTION: Want to Learn Affiliate Marketing from Successful Affiliates?
Join this FREE community where successful marketers share their secrets!
Learn directly from highly successful affiliate marketers
Access free, actionable training content regularly
Connect with an active community of over 5,000 members
Network with multiple six-figure earning affiliates
Get your questions answered by real experts
JOIN FREE NOW!
Keeping Records for Tax Reporting
Affiliate marketers need to keep thorough records for accounting and Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting purposes. Here’s a checklist of what to track:
- Commissions earned from each program
- Dates of payments received
- Expenses related to your affiliate marketing efforts (like website hosting and advertising)
- Any refunds or reversals you may encounter
Additionally, it’s wise to maintain documentation of all your transactions and communications with affiliate networks. This record-keeping not only helps when reporting taxes but also if any disputes arise, you can reference your documented evidence.
When reporting income, you’ll generally categorize it as business income, no matter if you’re a sole proprietor or part of a more complex business structure. If you are self-employed, you will file taxes using a Schedule C form which allows you to report your income and business expenses together.
Understanding the difference between gross income and net income is equally important. Gross income includes all the money you receive through affiliate marketing before expenses are deducted. Net income is what remains after subtracting your business expenses. Keeping track of both figures will help you understand your actual profit and how much tax you owe.
Another aspect you should consider is whether you need to make estimated tax payments. If you’re earning significant income from affiliate marketing, you may need to pay estimated taxes quarterly to avoid penalties. These payments are typically due in April, June, September, and January, and should be based on your expected total income for the year.
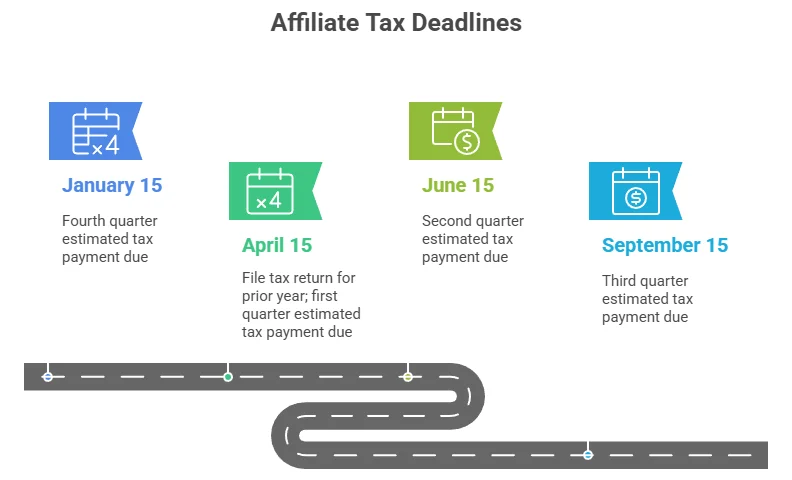
Key Estimated Tax Deadlines
Here is a brief overview of tax deadlines relevant to affiliate marketers:
| Deadline | Description |
|---|---|
| January 15 | Fourth quarter estimated tax payment due |
| April 15 | File tax return for prior year; first quarter estimated tax payment due |
| June 15 | Second quarter estimated tax payment due |
| September 15 | Third quarter estimated tax payment due |
To make the process easier, consider using accounting software specifically designed for freelancers and online marketers. Tools like QuickBooks or Zoho Books can help you organize your income and expenses seamlessly, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
You might also want to consult a tax professional who understands the ins and outs of affiliate marketing. They can offer tailored advice, help optimize your tax situation, and provide clarity on new laws that may affect your Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. Professional guidance might save you time and money in the long run.
Staying informed and organized is vital in navigating Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. By keeping accurate records, understanding your obligations, and utilizing helpful resources, you can make the tax season less daunting. Embrace the challenge, and remember: being proactive is the best strategy to mitigate surprises during tax time.
Common Misconceptions About Tax Obligations in Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing can be a rewarding venture, but many newcomers fall prey to common misconceptions regarding tax obligations. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for both compliance and peace of mind. Let’s explore some of the most frequent misunderstandings about Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting in the world of affiliate marketing.
Misconception: You Don’t Have to Report Affiliate Income
A widespread belief is that affiliate income is not taxable. This is far from the truth. In reality, any income earned through affiliate marketing is generally considered taxable income by the IRS. Whether you’re being paid through direct deposits, checks, or PayPal, you are required to report this income on your tax return. Failing to do so could lead to penalties and interest charges.
Misconception: Only Large Affiliates Need to Worry About Taxes
Another misconception is that taxes only concern high-earning affiliates. Regardless of how much money you make from affiliate marketing, you are still obligated to report it. Even small amounts can add up over time, and it’s best not to ignore them.
Misconception: All Affiliate Programs Provide 1099 Forms
Many assume that every affiliate program will send a 1099 form to report earnings. While it’s true that many reputable programs do, not all do so. If you earn less than $600 from a particular program during the year, they may not send you a 1099 form. It’s your responsibility to keep track of all your income, even if you do not receive official documentation.
Misconception: Business Expenses Can’t Be Deducted
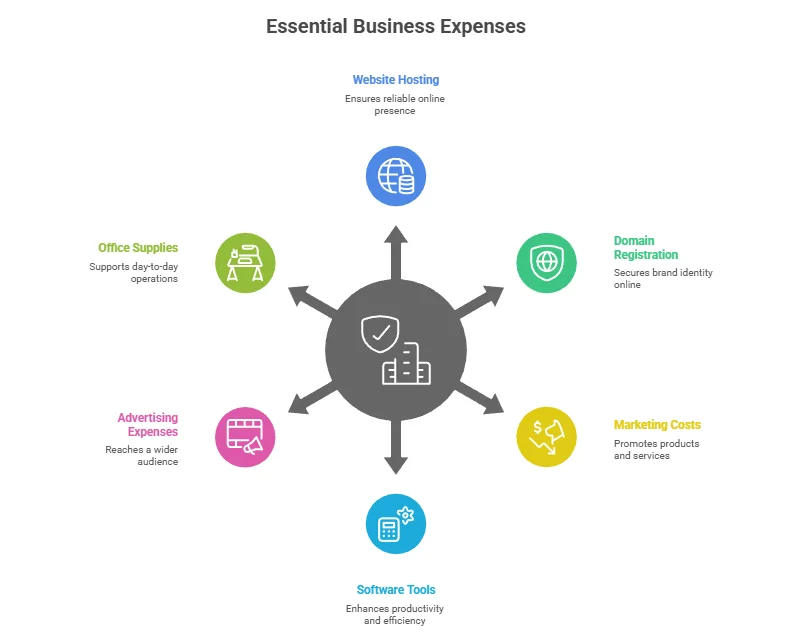
A common myth is that affiliate marketers cannot claim business expenses. In truth, you can deduct legitimate business expenses from your taxable income. These can include:
- Website hosting fees
- Domain registration
- Marketing costs
- Software tools
- Advertising expenses
- Office supplies and equipment
By tracking these expenses carefully, you can significantly lower your tax liability. This is an important part of correct Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting.
Misconception: You Can Just Wing It at Tax Time
Thinking that you can figure out your taxes without previous organization is another dangerous misconception. You should maintain accurate records throughout the year, including income, expenses, and receipts. Keeping everything in one place will save you a great deal of stress come tax time. Utilize tax software or consult a tax professional for insights tailored to your specific situation.
Misconception: States Don’t Tax Affiliate Income
Some affiliate marketers believe that only federal taxes apply to their income. However, many states also tax income, including earnings from affiliate marketing. Understanding your state’s regulations on income tax is vital. Check resources like Tax Foundation for insights specific to your state.
Misconception: You Can File Gains as Hobby Income
While it may feel like affiliate marketing is just a hobby, the IRS states that if you’re making money, it’s considered a business. You cannot just report it as hobby income, which usually has different tax rules and limits you on deductions. Treat your affiliate marketing as a business to ensure that you benefit from all available deductions and incentives.
Misconception: You Don’t Need Professional Help
Many new affiliate marketers feel confident handling their taxes without professional assistance. However, navigating the landscape of tax obligations can be tricky. Mistakes can lead to audits and financial repercussions. Consulting a qualified accountant or tax advisor, especially one familiar with affiliate marketing, can provide valuable guidance.
Keeping informed about tax obligations is essential for your affiliate marketing success. Stay educated, keep your records organized, and seek professional advice if needed. Don’t allow misinformation to hinder your financial growth. For more insights on Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting, you can visit IRS Affiliate Marketing or check out Accounting Coach for a deeper dive into expense deductions related to affiliate marketing.
How to Organize Your Affiliate Earnings for Tax Season
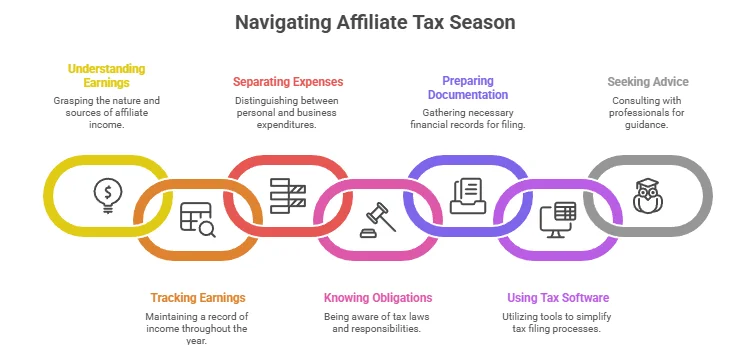
As tax season approaches, it’s essential for affiliate marketers to stay organized regarding their earnings. Properly managing your affiliate income can save you headaches when it comes time to file your taxes. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro in affiliate marketing, keeping clear and thorough records is key. Here’s how to manage your affiliate earnings effectively to prepare for Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting.
Understand Your Affiliate Earnings
The first step in organizing your affiliate earnings is understanding where your income is coming from. Most affiliate programs provide a dashboard where you can see your earnings. Common sources of income include:
- Pay-per-sale (PPS)
- Pay-per-click (PPC)
- Pay-per-lead (PPL)
- Recurring commissions
Each type of income may have different tax implications, so make sure you have a good grasp of how your affiliate partnerships operate.
Track Your Earnings Throughout the Year
Track your earnings consistently throughout the year rather than waiting until tax season. This will not only keep you organized but also help you understand your income trends.
Consider using spreadsheets or financial software to record the following:
- Date of transaction
- Amount earned
- Commission type
- Affiliate program
- Transaction IDs
Keeping a detailed record will make it easier to report your earnings accurately come tax time.
Separate Personal and Business Expenses
If you’re an affiliate marketer, you are likely running a business. Keeping your personal and business expenses separate is crucial for Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. Make it a habit to:
- Open a separate bank account for your affiliate earnings and expenses.
- Use dedicated software like QuickBooks to manage income and expenses.
- Store receipts for any business-related purchases to support your deductions.
Know Your Tax Obligations
As an affiliate marketer, you may be subject to different tax obligations based on your business structure, such as a sole proprietorship or LLC. Generally, when your earnings exceed a certain threshold (usually $600), you’ll receive a Form 1099 from the affiliate program, detailing your earnings for that year.
Be aware of the following:
- Self-employment tax rates
- Estimated quarterly tax payments
- State tax obligations
Make sure to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice tailored to your situation.
Prepare Your Documentation
When tax season arrives, having your documentation ready is vital. Make sure you have the following:
- 1099 forms from all affiliate programs
- Bank statements showing your affiliate income
- Receipts for business expenses
- Spreadsheet or summary of total earnings and expenses
This organized documentation will help streamline the process and reduce the chances of errors.
Consider Using Tax Software
There are several tax software options available that can simplify your Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. Programs like TurboTax and H&R Block are effective for organizing income and filing taxes. Look for features specifically for self-employed individuals, as they will help navigate compliance issues.
Seek Professional Advice
If managing your affiliate tax reporting feels overwhelming, consider hiring a tax professional. They can provide customized advice based on your unique situation and help you maximize deductions. This could save you money in the long run and ensure you comply with all tax laws.
Final Thoughts
Preparing your affiliate marketing earnings for tax season might seem daunting, but with organization and proactive tracking, you can make it manageable. Always keep your documentation in order and stay informed about your tax obligations. For more information and resources on managing affiliate marketing income, you may want to check out Shopify or Nolo. Following these guidelines will help you maintain your focus on growing your affiliate business while handling Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting smoothly.
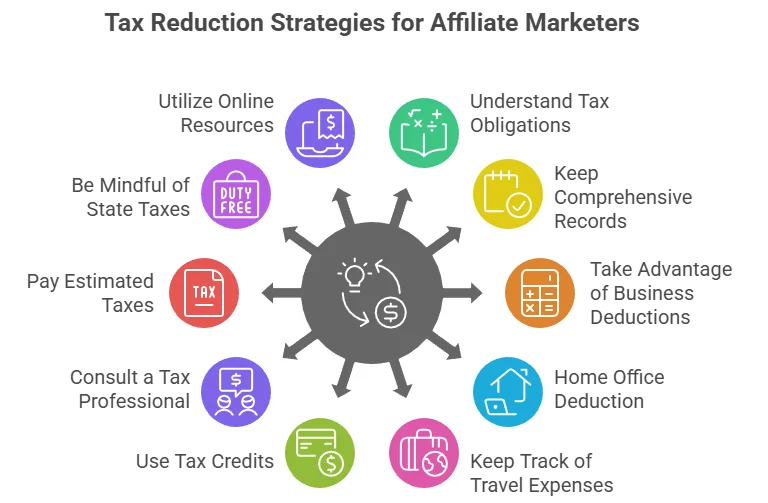
Tips for Reducing Your Tax Liability as an Affiliate Marketer
As an affiliate marketer, keeping more of your hard-earned income can be a game changer for your business. Understanding tax deductions and strategies to reduce your tax liability is crucial. Here are some tips to help you navigate the complex world of taxes while maximizing your revenue.
Understand Your Tax Obligations
First, it’s essential to grasp what you owe. The IRS considers affiliate marketing income as self-employment income. This means you’ll need to report it on your tax return. Be aware of the difference between an independent contractor and an employee to know how to classify your income correctly.
Keep Comprehensive Records
Maintaining accurate records is key. You should keep track of:
- Income generated from affiliate commissions
- Business-related expenses
- Transaction receipts
- Invoices sent to clients
Using accounting software can help you stay organized throughout the year. Software like QuickBooks or Xero can streamline your record-keeping process.
Take Advantage of Business Deductions
Many expenses are deductible when running an affiliate marketing business. Consider these common deductions:
- Website costs: This includes domain registration, hosting fees, or web development costs.
- Marketing expenses: Costs associated with paid advertisements, emails, or social media promotions.
- Office supplies: Items like computers, printers, and even office furniture may qualify.
- Education and training: If you invest in courses or seminars to improve your skills, you can deduct the expenses.
These deductions are vital for effective Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting.
Home Office Deduction
If you work from home, you might qualify for a home office deduction. This can include a portion of your mortgage or rent, utilities, and even home internet costs. However, make sure the space is exclusively used for your business.
Keep Track of Travel Expenses
Traveling for affiliate marketing can incur various expenses. Don’t forget to write off:
- Airfare or train tickets
- Hotel stays
- Meals during business trips (typically 50% deductible)
Ensure you keep receipts and a travel log to substantiate these costs during tax preparation.
Use Tax Credits
Look into tax credits that can reduce your tax liability. Some common credits include:
- Qualified Business Income Deduction: This allows eligible businesses to deduct 20% of their qualified business income.
- Credit for Small Employer Health Insurance Premiums: If you offer health insurance, you may be eligible for this credit.
Consult a Tax Professional
Navigating taxes can be overwhelming. Consulting a tax professional can save you time and money. They can ensure you are compliant with tax laws and maximize your deductions.
Pay Estimated Taxes
As an affiliate marketer, you might not have taxes withheld from your income. The IRS requires you to make estimated tax payments quarterly to avoid penalties. Make sure to calculate your estimated taxes based on your revenue and expenses.
Be Mindful of State Taxes
Your location may pose additional tax challenges. Some states have different rules and tax rates. Research your state’s requirements to ensure compliance and maximize your savings. Websites like Nolo offer valuable insights into state taxes.
Utilize Online Resources
Several online resources can assist you in understanding Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. Websites such as IRS – Self-Employed Individuals provide comprehensive tax guidelines that are crucial for affiliate marketers.
By understanding your tax obligations, keeping thorough records, and taking advantage of deductions and credits, you can effectively reduce your tax liability. Start implementing these strategies today to ensure your success as an affiliate marketer. Remember, savvy financial management can lead to greater profitability!
The Impact of Different Business Structures on Affiliate Marketing Taxes
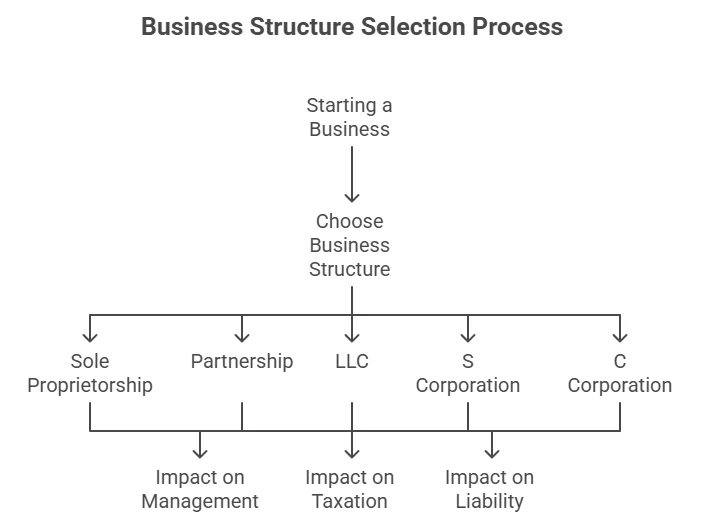
When engaging in affiliate marketing, it’s vital to understand how different business structures impact your taxes. The choice of business structure can influence everything from your tax rates to the type of forms you need to file. Here, we will explore the effects of various business types on Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting, helping you make an informed decision.
Sole Proprietorship
Operating as a sole proprietor is common among those starting in affiliate marketing. This structure is easy to set up and requires minimal paperwork. However, it comes with some tax implications:
- Tax Filing: You report affiliate earnings on your personal tax return, on Schedule C.
- Self-Employment Tax: You pay self-employment taxes which include Social Security and Medicare, totaling around 15.3%.
- Deductions: You can take business deductions for expenses such as web hosting, advertising costs, and any tools that assist in your marketing efforts.
Partnership
If you team up with another person in affiliate marketing, you might form a partnership. This structure offers both advantages and disadvantages:
- Flow-Through Taxation: Profits pass through to partners, who report earnings on their tax returns.
- Self-Employment Taxes: Like sole proprietors, partners also pay self-employment taxes on their share of earnings.
- Partnership Agreement: It’s advisable to outline how profits and losses are shared to avoid future disputes.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Many affiliate marketers opt for an LLC due to its flexibility and liability protection. This structure can impact taxes in several ways:
- Pass-Through Taxation: By default, LLCs are treated like sole proprietorships or partnerships, ensuring profits are reported on owners’ personal tax returns.
- Tax Flexibility: LLCs can elect to be taxed as an S corporation or C corporation, which can lower self-employment taxes.
- Liability Protection: Members are protected from personal liability for business debts, which is a significant benefit.
S Corporation
Forming an S Corporation can offer tax advantages for affiliate marketers earning over a certain threshold:
- Dividend Distribution: Profits can be distributed as dividends, often taxed at a lower rate than regular income.
- Salary Requirement: Owners must pay themselves a reasonable salary, which is subject to self-employment tax, but dividends are not.
- Increased Scrutiny: The IRS scrutinizes S Corporations more closely, so ensure compliance with regulations.
C Corporation
A C Corporation can be beneficial for those planning to expand but comes with a different tax structure:
- Double Taxation: C Corporations are taxed at the corporate level, and dividends are taxed again on shareholders’ tax returns.
- Employee Benefits: C Corporations can offer various employee benefits that might reduce taxable income.
- Complex Reporting: They require more paperwork and formalities, including corporate tax returns.
Understanding your business structure will significantly affect your Affiliate Marketing Tax Reporting. You may want to consult with a tax advisor or accountant to analyze your situation and make informed decisions. Here are a few resources to explore further:
Your choice of business structure significantly impacts how you report taxes for your affiliate marketing endeavors. By understanding these differences, you can optimize your tax situation and minimize your liabilities effectively.
